Hippo
Lord Hippo
- Posts
- 55,972
Some time ago I tested my Freelanders battery charging circuit and thought you lot would find the results interesting. This was done using an oscilloscope (scope). A scope measures voltage against time. Voltage is vertical and time is horizontal. A scope measures voltage just like a volt meter (multimeter) does. The advantage of a scope is that it displays the result in the form of a graph.
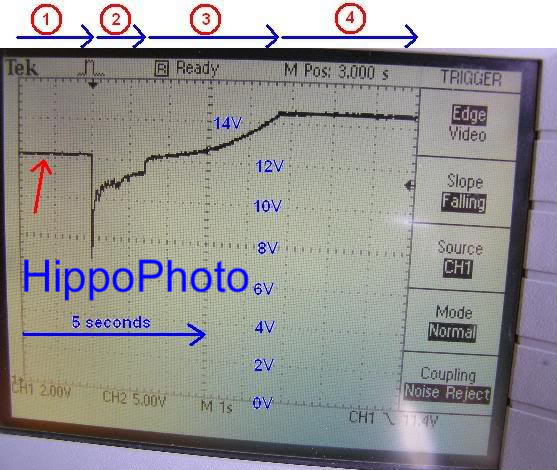
The scope trace (arrowed red) shows the voltage of my Freelanders battery whilst idle, starting and charging, with respect to time.
Phase 1 shows the battery voltage after the ignition has been switched on. The fuel pumps have already been primed and the computers pre starting checks have completed. Hence the battery voltage is stable at about 12.2volts as there's only a small load on the battery to power the computer electrics.
Phase 2 shows the battery voltage during engine starting when the ignition key is turned. You'll notice the battery volts drop to about 7volts momentarily due to the sudden impact of the induced load on the battery, as the starter motor is first powered. This is the bit where the battery has to supply a sudden load current of several hundred amps. Starting takes about 1.4 seconds to complete. The battery voltage is approx 11volts during starting due to the significant load current required to power the starter motor. The onboard computers need a minimum of 9volts for them to stay alive, but they're able to cope with the sudden volt drop below 9volts as it's only for a fraction of a second. The voltage drops as the battery doesn't have the capacity to be able to supply such a large amount of current, whilst maintaining it's output voltage, whilst powering the starter motor.
Phase 3 shows the battery voltage when the engine is running, just after the engine was started. In order for the alternator to start charging the battery it must generate a voltage higher than the batteries output terminal voltage. Hence the voltage rises during phase 3 while the alternator output voltage increases, whilst pushing the battery voltage higher, as it overcomes the batteries current charge state. That takes about 3.1 seconds. Normally the alternator would give out its maximum voltage straight away, but this is loaded by the battery so it's dragged down temporally.
Phase 4 shows the alternator is charging at its maximum output voltage of about 14.5volts. The scope is an expensive device which is calibrated so it's fairly precise.
enginestart wRjLvgN.jpg
The measurements shown above were recorded after the battery had purposely been discharged a bit. That gives you better results of what's happening as you can see the charge of the alternator pushing the battery terminal voltage higher, as the alternator starts producing electricity, and the battery starts charging.
The scope trace (arrowed red) shows the voltage of my Freelanders battery whilst idle, starting and charging, with respect to time.
Phase 1 shows the battery voltage after the ignition has been switched on. The fuel pumps have already been primed and the computers pre starting checks have completed. Hence the battery voltage is stable at about 12.2volts as there's only a small load on the battery to power the computer electrics.
Phase 2 shows the battery voltage during engine starting when the ignition key is turned. You'll notice the battery volts drop to about 7volts momentarily due to the sudden impact of the induced load on the battery, as the starter motor is first powered. This is the bit where the battery has to supply a sudden load current of several hundred amps. Starting takes about 1.4 seconds to complete. The battery voltage is approx 11volts during starting due to the significant load current required to power the starter motor. The onboard computers need a minimum of 9volts for them to stay alive, but they're able to cope with the sudden volt drop below 9volts as it's only for a fraction of a second. The voltage drops as the battery doesn't have the capacity to be able to supply such a large amount of current, whilst maintaining it's output voltage, whilst powering the starter motor.
Phase 3 shows the battery voltage when the engine is running, just after the engine was started. In order for the alternator to start charging the battery it must generate a voltage higher than the batteries output terminal voltage. Hence the voltage rises during phase 3 while the alternator output voltage increases, whilst pushing the battery voltage higher, as it overcomes the batteries current charge state. That takes about 3.1 seconds. Normally the alternator would give out its maximum voltage straight away, but this is loaded by the battery so it's dragged down temporally.
Phase 4 shows the alternator is charging at its maximum output voltage of about 14.5volts. The scope is an expensive device which is calibrated so it's fairly precise.

enginestart wRjLvgN.jpg
The measurements shown above were recorded after the battery had purposely been discharged a bit. That gives you better results of what's happening as you can see the charge of the alternator pushing the battery terminal voltage higher, as the alternator starts producing electricity, and the battery starts charging.
Last edited:
